Single-cell gene expression profiling is fundamentally reshaping our understanding of biology at a granular level. Unlike conventional bulk RNA sequencing, which smooths out the complexities by averaging gene expression across a broad group of cells, single-cell profiling digs deep into the gene activity of individual cells. This allows us to unlock insights into the intricate diversity that exists within cellular populations, a feat previously unimaginable. The potential of this technology is vast, extending across disease research, drug development, and various biological fields.
In this article, we’ll dive into the techniques driving this revolution, examine its diverse applications, tackle the challenges that come with it, and explore where this technology is headed. Along the way, we’ll compare it to traditional bulk RNA sequencing to highlight the distinct advantages and limitations. By the end, you’ll have a clear grasp of why single-cell gene expression profiling is a pivotal breakthrough in molecular biology and genomics.
What is Single-Cell Gene Expression Profiling?
Single-cell gene expression profiling represents a transformative advancement in molecular biology, enabling unprecedented resolution in the analysis of gene activity at the individual cellular level. Whereas traditional bulk RNA sequencing obscures cellular heterogeneity by aggregating transcriptomic data across populations, this methodology interrogates the transcriptional landscape of singular cells, exposing the intricate biological diversity inherent to tissues. Such granularity permits the identification of rare cell subtypes, the characterization of context-dependent cellular responses, and the detection of subtle expression patterns that bulk approaches invariably mask.
Central to this paradigm is single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), a technique that facilitates transcriptome-wide profiling of individual cells. By circumventing the averaging effects inherent to population-level analyses, scRNA-seq reveals stochastic and regulated gene expression variability, offering critical insights into cellular states and functions. Analogous to high-resolution imaging at the molecular scale, this technology elucidates features of biological systems- such as transient transcriptional bursts or clonal heterogeneity in disease- that remain inaccessible to conventional methods.
The implications are profound. In oncology, single-cell profiling disentangles tumor microenvironments by identifying rare malignant subclones or immunosuppressive stromal cells. In developmental biology, it maps lineage trajectories with cellular precision. Even in ostensibly homogeneous cell populations, it uncovers functional mosaicism, challenging long-held assumptions about cellular uniformity. While technical challenges persist- including computational demands for analyzing high-dimensional datasets and the need for standardizing the capacity to deconstruct biological complexity at this resolution has already redefined investigative frameworks in immunology, neurobiology, and regenerative medicine.
By bridging the gap between genomic potential and phenotypic manifestation, single-cell gene expression profiling transcends mere technical innovation; it represents a fundamental shift in how biological systems are conceptualized and studied.

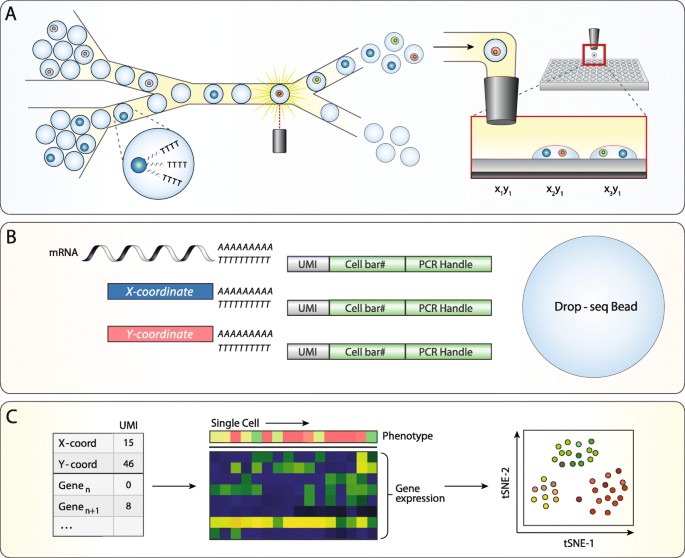
A high-throughput platform for linked optical phenotype and gene expression of single cells. Jesse Q. Zhang et al,. 2020)
Key Techniques in Single-Cell Gene Expression Analysis
The landscape of single-cell gene expression analysis has evolved dramatically over the past few years, driven by a suite of advanced techniques that provide unprecedented insights into the molecular makeup of individual cells. These methods uncover the unique features of cellular diversity, helping scientists gain deeper insights into everything from rare cell types to intricate gene regulatory networks. Let’s explore the most pivotal techniques shaping this exciting field.
scRNA-seq
scRNA-seq has emerged as a cornerstone of modern cellular genomics, offering unparalleled resolution in dissecting transcriptional heterogeneity at the individual cell level. In contrast to conventional bulk RNA sequencing, which obscures cell-to-cell variability by averaging transcriptomic signals across populations, scRNA-seq interrogates the molecular identity of singular cells, revealing dynamic expression patterns critical to understanding cellular function and dysfunction. This granular resolution has proven transformative in oncology, where it has unmasked tumor microenvironments as mosaics of clonal diversity, elucidating subpopulations with divergent therapeutic vulnerabilities. Besides, a seminal 2016 study by Tirosh et al. (Science) exemplifies this capability, identifying transcriptionally distinct glioblastoma cell states linked to adaptive drug resistance mechanisms, thereby reshaping therapeutic target prioritization.
Beyond oncology, scRNA-seq has catalyzed the discovery of rare and transitional cell states across biological systems. In immunology, it has resolved cryptic subsets of immune cells driving pathological inflammation, while in developmental biology, it has delineated lineage bifurcations with single-cell precision. Traditional bulk approaches, constrained by their inability to deconvolve minority populations, often fail to detect these critical actors. scRNA-seq revealed novel dendritic cell subsets controlling antigen presentation and neuro-immune crosstalk, impacting vaccines and autoimmune therapies.
Nevertheless, challenges persist. Robust pipelines and normalization overcome high-dimensional challenges, making scRNA-seq a lens for linking transcription to function.
Learn more: