Learn practical encryption techniques for business to secure sensitive data. A complete guide for IT teams to implement effective data protection strategies.
Why Businesses Can’t Ignore Encryption
Imagine this: a small e-commerce company stores thousands of customer records, including payment information. One day, hackers gain access to the network. Without encryption, all that sensitive data would be exposed, leading to lost revenue, lawsuits, and damaged trust.
This is where encryption techniques for business come into play. Encryption isn’t just a technical buzzword—it’s a practical tool that safeguards data, builds customer confidence, and ensures regulatory compliance. In this guide, we’ll break down the main encryption methods and show you how businesses can apply them effectively.
Symmetric Encryption: Speed Meets Security
Symmetric encryption uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt data. Its speed makes it ideal for handling large volumes of information.
- Popular Algorithms: AES, DES, 3DES
- Best For: Encrypting databases, file storage, and backups
- Pros: Fast, efficient, and suitable for bulk data
- Cons: Key distribution can be tricky; everyone sharing the key must keep it secure
Example: A retail business encrypts its sales database using AES. Employees can quickly access encrypted files while keeping sensitive customer information safe from breaches.
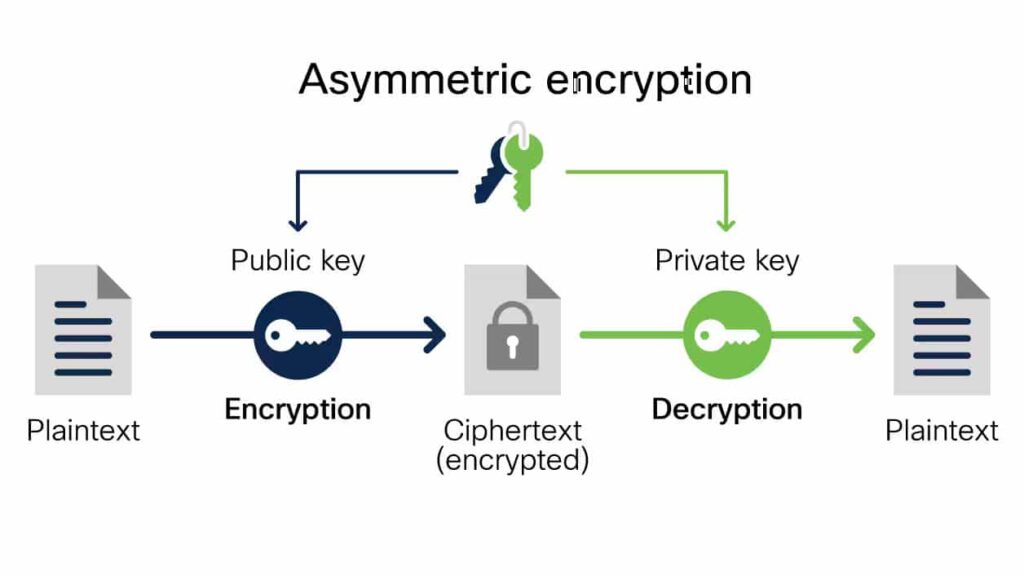
Asymmetric Encryption: Securing Communication
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- Popular Algorithms: RSA, ECC
- Best For: Email encryption, secure transactions, and digital signatures
- Pros: Safe key distribution, ideal for communication between parties
- Cons: Slower than symmetric encryption; not suitable for large datasets
Example: When a business sends sensitive contracts to clients via email, asymmetric encryption ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read the message.
Hashing: Protecting Data Integrity
Hashing is a one-way encryption technique that converts data into a fixed-length string. Unlike other methods, hashed data cannot be reversed, making it ideal for verifying integrity.
- Popular Algorithms: SHA-256, MD5
- Best For: Password storage, file verification, digital signatures
- Pros: Confirms data hasn’t been tampered with
- Cons: Cannot retrieve original data from the hash
Example: Online services store user passwords as hashes. Even if the database is compromised, the actual passwords remain protected.
Hybrid Encryption: Combining Strengths
Hybrid encryption merges the speed of symmetric encryption with the security of asymmetric encryption.
- How It Works: Asymmetric encryption secures the key exchange, then symmetric encryption encrypts the bulk data
- Best For: Cloud storage, secure messaging, and file transfers
- Pros: Efficient and highly secure
- Cons: Slightly more complex to implement
Example: Cloud storage providers encrypt files with AES while securing the keys with RSA, ensuring quick access without sacrificing security.
Practical Steps for Businesses
- Identify sensitive data: Determine what needs protection based on regulatory and operational requirements.
- Select the right encryption type: Use symmetric for large datasets, asymmetric for secure communication, and hybrid for a balanced approach.
- Implement secure key management: Protect, rotate, and monitor encryption keys regularly.
- Educate staff: Train employees on safe handling of encrypted data and secure communication practices.
- Monitor and audit systems: Regularly check encryption effectiveness and ensure compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
Conclusion: Make Encryption Techniques a Business Priority
For businesses today, understanding encryption techniques for business is more than a technical necessity—it’s a strategic advantage. By implementing the right encryption methods, managing keys securely, and educating your team, you can protect sensitive data, comply with regulations, and maintain trust with clients and partners.
Start applying these encryption techniques today to safeguard your business and stay ahead of evolving cybersecurity threats.