Rates & Model Comparison
Understanding Tokens, Costs, and Optimization Strategies for 2025
Large language models are now deeply embedded in business software. That’s why figuring out their pricing is important for developers, product managers, and organizations. Unlike traditional licensing, LLM APIs work on a consumption model, built around a key unit: the token. This guide makes LLM API costs clear, covering all, from basic token ideas to advanced optimization methods, while helping readers understand bold, budget-friendly insights aligned with modern LLM API pricing.
The LLM API landscape in 2025 includes key providers like OpenAI, Anthropic’s Claude, Google’s Gemini, and xAI’s Grok. Each has distinct pricing, capabilities, and use cases.. By the end of this guide, you’ll know how to calculate costs accurately, choose the right model, and apply strategies that can reduce your AI spending by up to 90%.
Discover how enterprises streamline model orchestration with our multi-llm platform for enterprises.
What is a Token?
A token is the fundamental unit that LLMs use to process text, and it plays a role in LLM API pricing. Rather than reading character by character or word by word, language models break text into smaller chunks called tokens. These tokens are the atomic units upon which all LLM processing and billing are based, affecting overall LLM token cost.
How Tokenization Works
When you send text to an LLM, the model’s tokenizer breaks it apart. It uses algorithms like Byte-Pair Encoding for this. Different models use different tokenizers, you see. This means the same text can create different token counts depending on your provider, which can influence LLM API cost. It’s a bit unpredictable. But as a general rule, you’ll find that:
- 1,000 tokens approximately equals 750 words in English
- One token roughly corresponds to 4 characters of English text
- A typical page of text (500 words) uses approximately 666 tokens
- Non-English languages often require more tokens per word
- Code and special characters may tokenize differently from natural language
For example, the sentence “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog” might be tokenized as:

resulting in 9 tokens. Notice how spaces are often attached to the following word as part of the same token.
Why Tokens Matter for Pricing?
This approach neatly ties your costs directly to the computing resources used. More tokens mean more processing power, more memory, and more time. We believe this model is great for developers because it offers such detailed cost control in LLM API pricing. You only pay for what you use, honestly. That makes it wonderfully feasible to scale from a tiny test to a huge, company-wide deployment.
Explore our AI strategy consulting & machine learning services to plan and scale your enterprise AI initiatives.

Understanding Input and Output Tokens
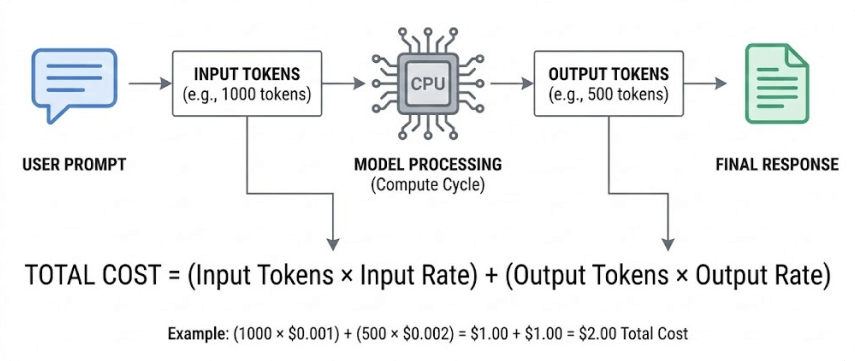
Providers distinguish between two types of tokens, each priced differently to reflect the computational resources required in LLM API pricing.
Input Tokens (Prompt Tokens)
Input tokens represent all the text you send to the model, including:
- System prompts and instructions
- User messages and queries
- Context documents and reference materials
- Conversation history in multi-turn chats
- Few-shot examples
- Tool and function definitions
Input tokens are generally less expensive than output tokens because the model only needs to process and understand them, not generate new content, which influences overall LLM API cost.
Read More: https://mobisoftinfotech.com/resources/blog/ai-development/llm-api-pricing-guide



