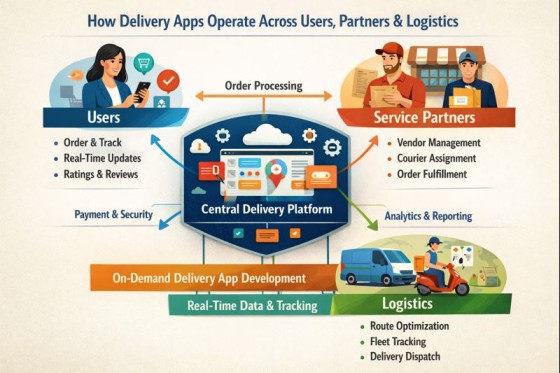
The rapid expansion of digital commerce has transformed how goods and services reach consumers. Delivery platforms now act as intermediaries that connect users, service partners, and logistics networks within a single operational ecosystem. Understanding these mechanisms requires examining technical architecture, operational workflows, and stakeholder coordination. This article explains how such platforms function end to end, with particular attention to how on demand delivery app development supports scalability, reliability, and user satisfaction in highly competitive markets while balancing operational complexity and evolving consumer expectations.
Evolution of Multi Sided Delivery Platforms in Digital Commerce
Delivery platforms originated as simple ordering interfaces but have evolved into multi sided systems integrating consumers, merchants, and couriers. This evolution was driven by demand for convenience, speed, and transparency. Early models focused primarily on user ordering, while modern platforms manage complex interactions across several participants simultaneously.
Key evolutionary stages include:
- Transition from single merchant ordering to aggregated marketplaces
- Integration of real time logistics and location tracking
- Adoption of modular system architectures for faster updates
From a technical standpoint, on demand delivery app development enables these platforms to coordinate data flows among users, partners, and logistics providers in real time. This coordination ensures that availability, pricing, and delivery timelines remain accurate across the ecosystem.
User Experience Design Principles Shaping Consumer Ordering Behavior
User experience design plays a critical role in determining how consumers interact with delivery platforms. Interfaces must be intuitive while supporting complex decision making, such as selecting vendors, comparing prices, and tracking orders.
Effective platforms prioritize:
- Clear navigation and minimal steps to complete an order
- Real time order status visibility
- Consistent performance across devices
Design teams rely on behavioral analytics to refine layouts and workflows. These insights inform interface adjustments that reduce abandonment rates and improve satisfaction. While the underlying technology is complex, the goal is to make the experience feel effortless for users, masking the operational intricacy behind the scenes.
Partner Onboarding Models and Operational Controls for Providers
Service partners, including merchants and couriers, are essential contributors to delivery platforms. Efficient onboarding ensures that partners can begin operations quickly while complying with platform standards.
Common onboarding components include:
- Verification of business credentials and service capabilities
- Training on order management and communication tools
- Performance benchmarks and compliance requirements
Platforms often support flexible deployment models, such as a white label delivery app, allowing partners to operate under a unified system while maintaining their own branding. Operational controls help ensure consistent service quality, manage disputes, and enforce platform policies without disrupting day to day operations.
Order Lifecycle Management From Placement to Final Fulfillment
The order lifecycle represents the core operational workflow of a delivery platform. It begins when a user places an order and ends with successful fulfillment and feedback collection.
Typical lifecycle stages involve:
- Order placement and confirmation
- Partner acceptance and preparation
- Courier assignment and pickup
- Delivery completion and review
Each stage relies on automated decision engines and real time communication. Systems must account for exceptions such as delays, cancellations, or substitutions. Accurate lifecycle management improves reliability and builds user trust, which is critical for repeat engagement.
Logistics Coordination and Real Time Fleet Optimization Mechanisms
Logistics coordination is one of the most technically demanding aspects of delivery platforms. Real time fleet optimization ensures that couriers are allocated efficiently while minimizing delivery times and operational costs.
Core mechanisms include:
- GPS based tracking and route optimization
- Dynamic courier assignment algorithms
- Load balancing during peak demand periods
These systems analyze traffic patterns, courier availability, and order density. By continuously recalculating optimal routes, platforms can respond quickly to disruptions and maintain service consistency even during high volume periods.
Data Architecture Security Standards and Regulatory Compliance Factors
Behind every delivery platform lies a robust data architecture designed to handle high transaction volumes securely. Sensitive information such as payment details, location data, and personal identifiers must be protected at all times.
Critical considerations include:
- Secure data storage and encryption practices
- Compliance with regional data protection regulations
- Controlled access for partners and internal teams
Scalable data architectures also support analytics and reporting, enabling platforms to monitor performance and detect anomalies. Strong governance frameworks help maintain trust among users and partners while reducing legal and operational risks.
Cost Structures Scalability Considerations and Deployment Approaches
Managing financial sustainability requires careful planning of cost structures and scalability strategies. Infrastructure, development, and ongoing maintenance contribute significantly to overall expenditure.
Key cost drivers typically involve:
- Cloud infrastructure and data management
- Continuous feature enhancement and testing
- Support and operational oversight
Organizations often evaluate delivery app development cost in relation to expected transaction volume and growth rate. Modular deployment approaches and standardized mobile app development solutions allow platforms to scale incrementally without extensive reengineering. For early stage validation, some teams rely on MVP app development services to test assumptions before committing to full scale implementation.
Future Trends Influencing Platform Efficiency and Market Expectations
Delivery platforms continue to adapt as technology and consumer expectations evolve. Automation, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics are shaping the next phase of platform efficiency.
Emerging trends include:
- Increased use of demand forecasting models
- Greater emphasis on sustainability and route efficiency
- Deeper integration with external commerce ecosystems
These developments aim to improve responsiveness while reducing operational strain. As platforms mature, their success will depend on balancing innovation with reliability and transparent stakeholder coordination.
Conclusion
Delivery platforms operate through a carefully orchestrated interaction of technology, operations, and stakeholder management. By aligning user experience, partner workflows, and logistics execution within a secure and scalable framework, these systems deliver consistent value across complex networks. A clear understanding of these mechanisms provides insight into how modern digital marketplaces function and how they continue to adapt to changing market dynamics and consumer expectations.